HCRMP: A LLM-Hinted Contextual Reinforcement Learning Framework for Autonomous Driving
Collaborating student: Zhiwen Chen, 1st-year Ph.D. Student.
Motivation
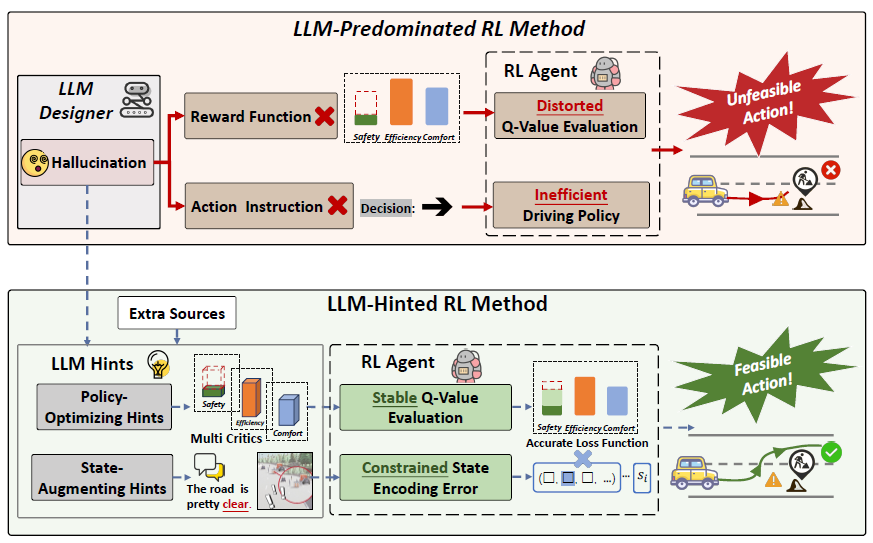
Integrating the understanding and reasoning capabilities of Large LanguageModels (LLM) with the self-learning capabilities of Reinforcement Learning (RL) enables more reliable driving performance under complex driving conditions. However, there is a strong reliance of current RL methods on LLM outputs and these methods are strongly influenced by the LLM hallucinations.
We argue that maintaining relative independence between the LLM and the RL agent is vital for solving the hallucinations problem. An LLM-Hinted RL motion planning paradigm is proposed, and an architecture called HCRMP (LLM-Hinted 72 Contextual Reinforcement Learning Motion Planner) is developed.
Highlights
- We explain the strong reliance on LLM outputs, and highlight the problem that hallucinations from the LLM can degrade driving performance. we propose the LLM-Hinted RL paradigm to address these challenges.
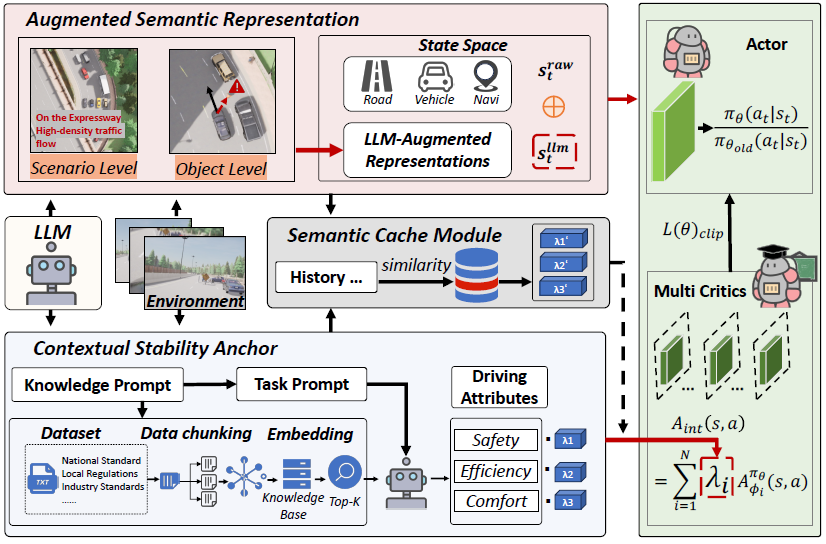
- We propose a novel motion planning architecture named HCRMP. By combining the semantic hints for policy optimization and state augmentation provided by LLM with the self-learning capabilities of RL, it significantly improves driving performance in diverse driving conditions.
Some Results
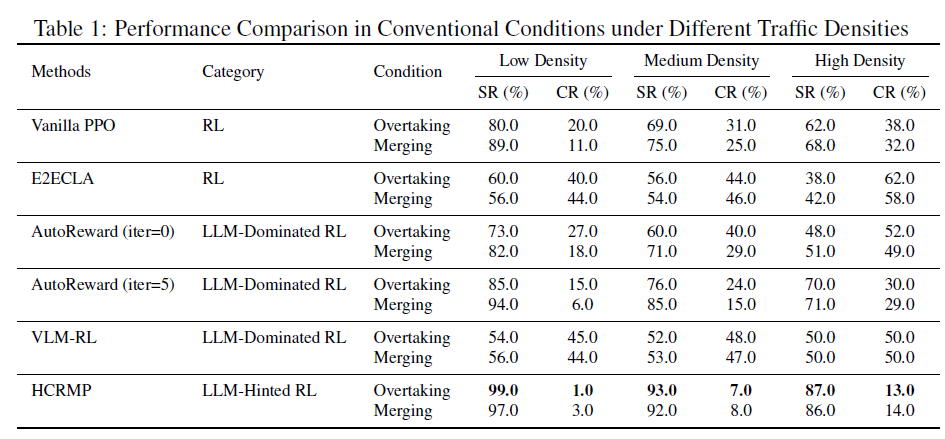
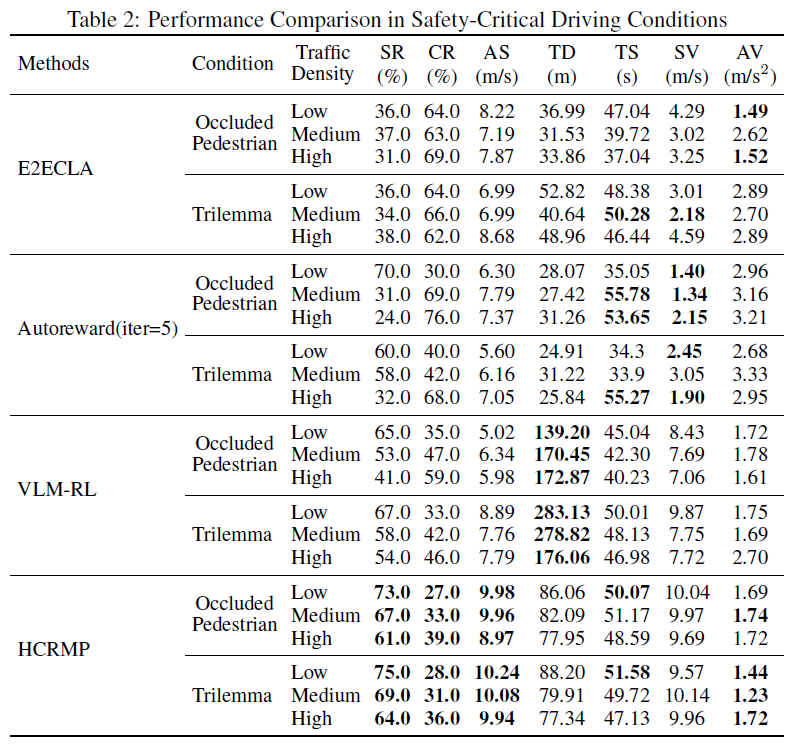
HCRMP matches or outperforms other baselines in different driving conditions, particularly in medium- and high-density driving conditions, where it achieves an average success rate of 89.5%.
Submitted/In Progress:
- HCRMP: A LLM-Hinted Contextual Reinforcement Learning Framework for Autonomous Driving, Zhiwen Chen, Hanming Deng, Zhuoren Li*, Huanxi Wen, Guizhe Jin, Ran Yu and Bo Leng*, Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2025. (accept)