Uncertainty-aware safe RL for safety-critical decision and control with high-order CBF
Collaborating student: Ran Yu, 1st-year Gruaduate Student.
Motivation
CBF-RL has become popular in the field of safe RL control in recent years. However, due to the high relative degree between the standard CBF and the underlying system control inputs, the safety can be compromised due to the inability to constrain the higher-order dynamics resulting in transient transgressions of the lower-order constraints.
Additionally, cognitive limitations and environmental randomness can lead to unreliable decisions in safety-critical scenarios. The estimated uncertainty of RL policy can provide a design basis for the dynamic adjustment of CBF constraints.
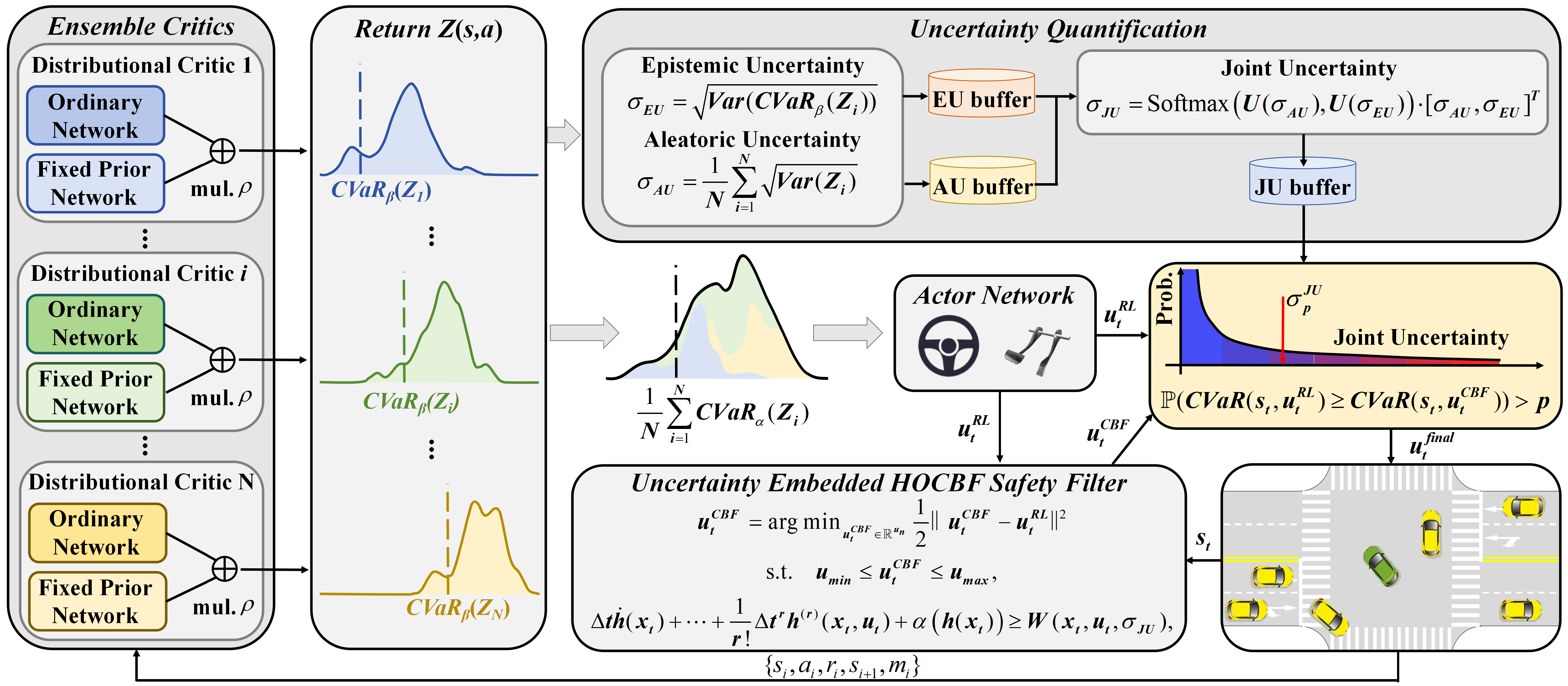
Therefore, this work generates a risk-averse policy by constructing a risk-aware ensemble distributional RL, while estimating uncertainty to quantify the policy’s reliability. A high-order control barrier function (HOCBF) is employed as a safety filter to minimize intervention policy while dynamically enhancing constraints based on uncertainty.
Highlights
- Propose a risk-aware distributional RL ensemble architecture that combines the original and Fixed Prior Networks (FPN) to build the critic. It quantifies tail risk in the reward distribution and generates a risk-averse policy, while jointly estimating epistemic uncertainty and aleatoric uncertainty for dual uncertainty-driven decision-making.
- A high-order control barrier function (HOCBF) is constructed, which ensures safety using only relative distance. Moreover, HOCBF incorporates JU to dynamically adjust safety constraints, balancing safety and traffic efficiency.
Some Results
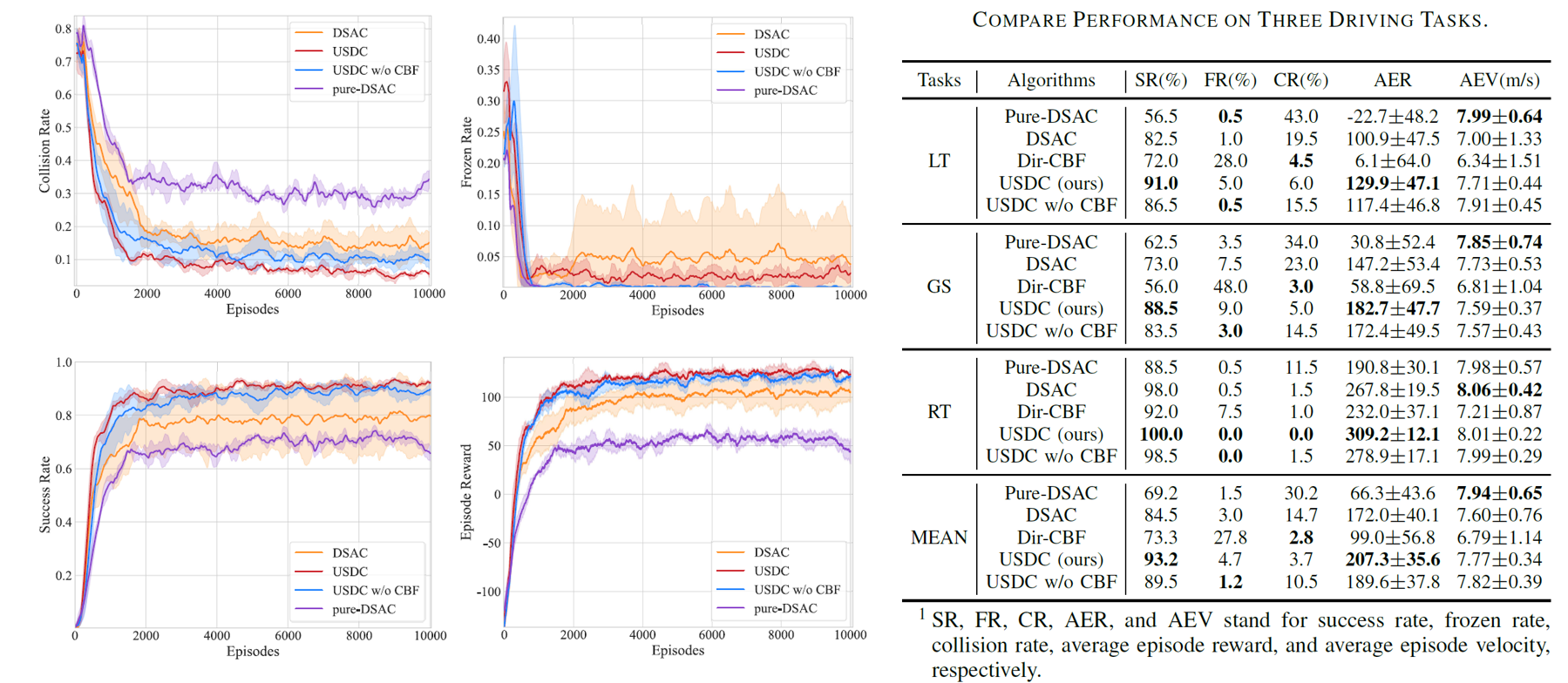
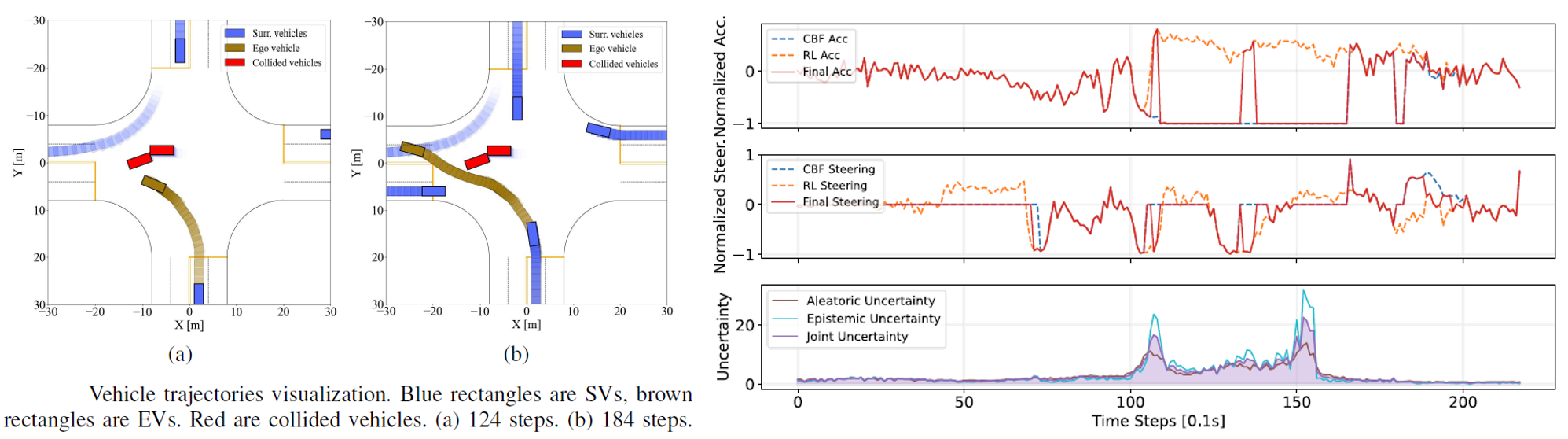
More details can be found in our recent paper “Uncertainty-Aware Safety-Critical Decision and Control for Autonomous Vehicles at Unsignalized Intersections.” (under review) PDF
Safe DRL with risk evaluation and dangerous momry enhancement
Collaborating student: Guizhe Jin, 2st-year Gruaduate Student.
Motivation
Evaluating the anticipated safety risk in the long time domain can provide better safety guidance for driving behavior decisions. Explicitly constructing future trajectories corresponding to RL actions coudld make it conveniently combined with risk evaluation.
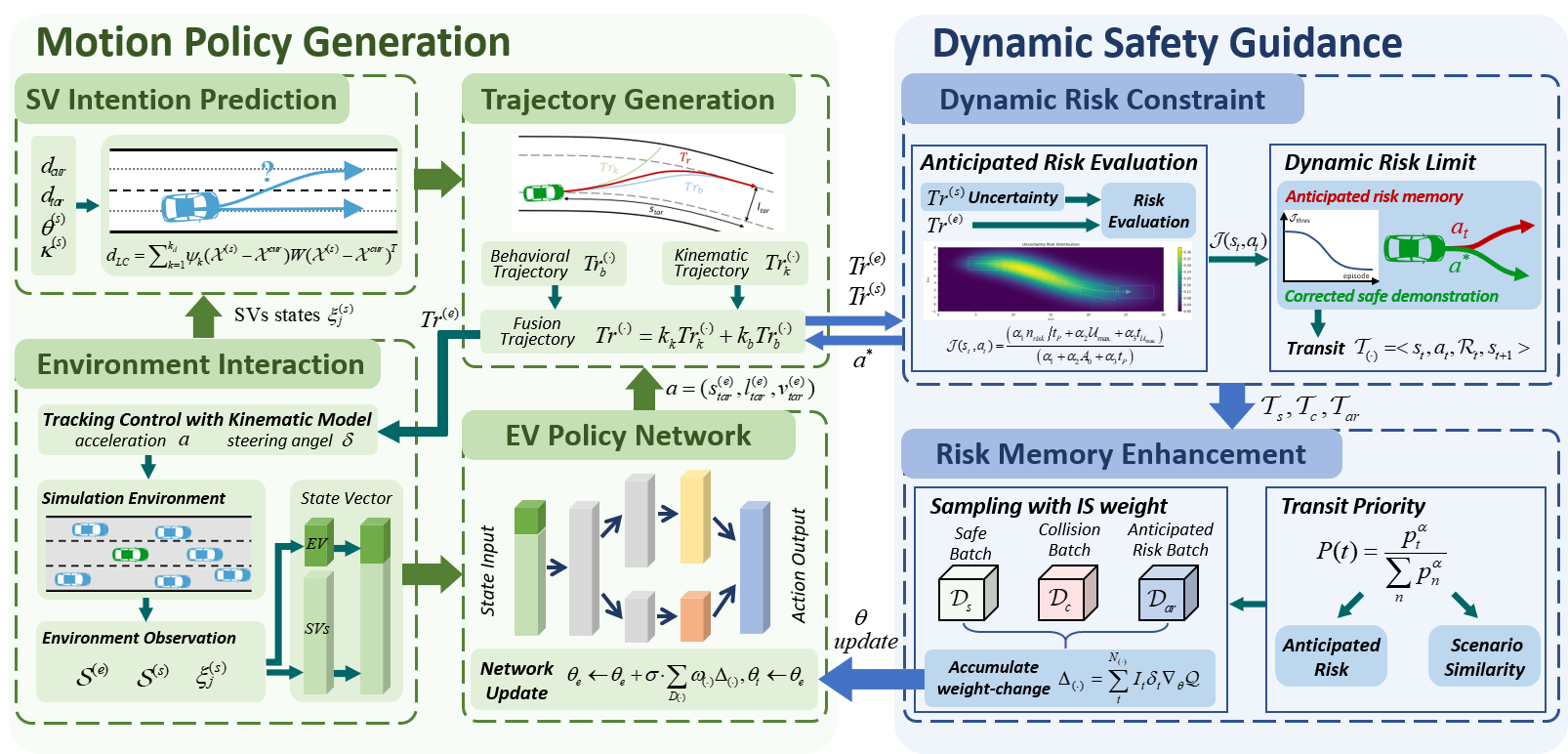
Proposeing a safety enhanced deep reinforcement learning for autonomous motion planning in lane-changing maneuver. The goal of this work is to design a DRL motion planner, which dares to make mistakes to learn the safe driving policy faster and better.
Highlights
- Evaluate the future motion risk by projecting DRL behavior action into the feasible trajectory, while sorrunding vehicles’ trajecotires are obtained from the prediction module.
- Dangerous action will be prevented and the dangerous virtual experiences are recoreded to gain various valuable experience data.
- Dangerous experiences are sampled with priority weight according their anticipated risk, enabling DRL agnet to learn a safer policy.
Some Results
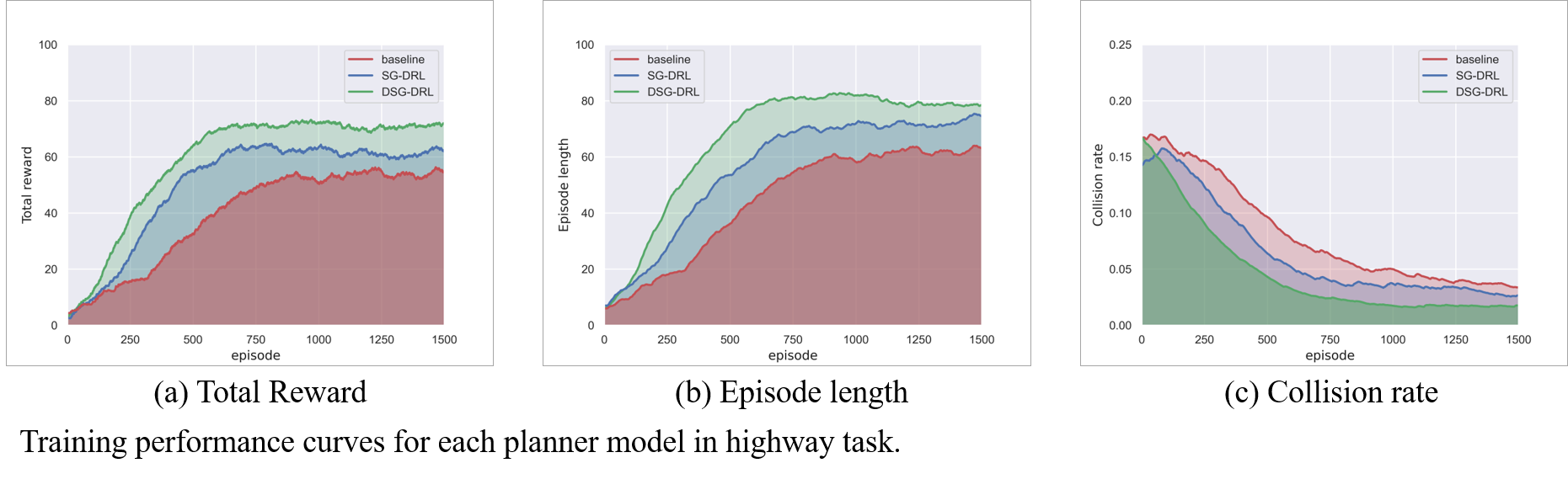
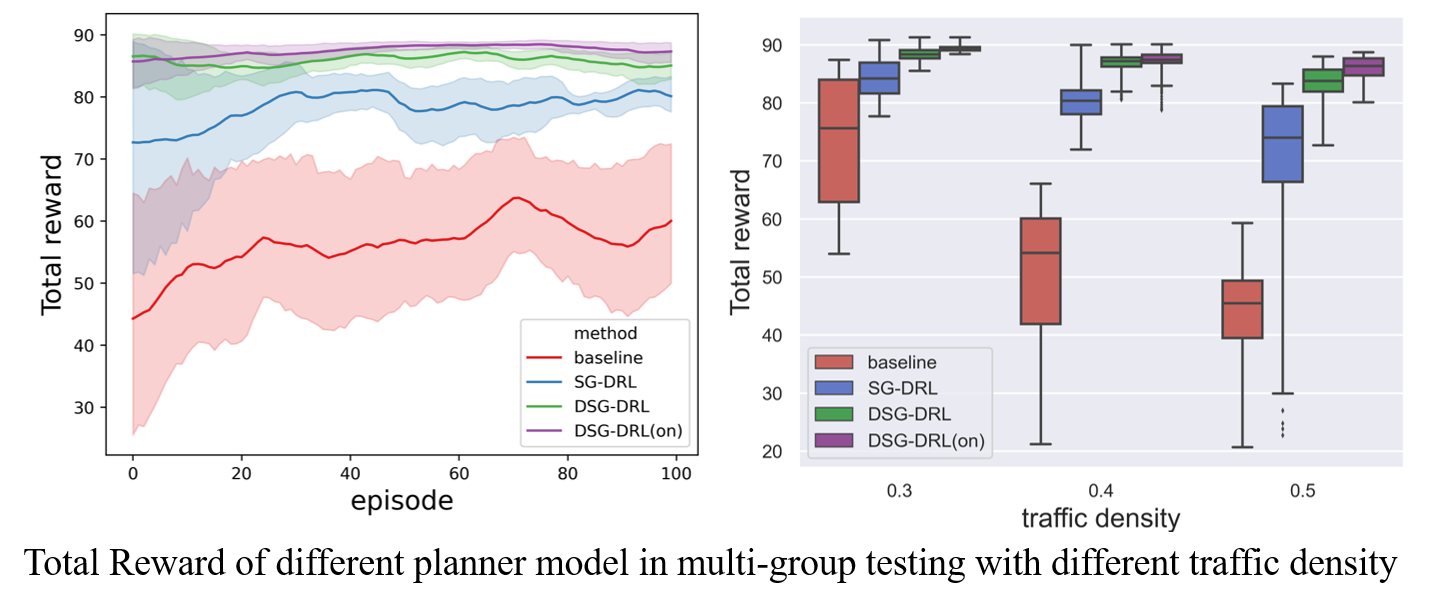
 Proposing safety enhanced DRL approach could improve the driving performance, espeacially in safety metrics such as reducing collision rate, anticipated risk, etc.
Proposing safety enhanced DRL approach could improve the driving performance, espeacially in safety metrics such as reducing collision rate, anticipated risk, etc.
More details can be found in our recent paper “Safety Enhanced Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving: Dare to Make Mistakes to Learn Faster and Better”. (under review, it will come soon) and “Safe Reinforcement Learning of Lane Change Decision Making with Risk-Fused Constraint”. PDF, DOI.
Risk-awre RL based on Safe Critic and Iterative Action Correction
Collaborating student: Ran Yu, 1st-year Gruaduate Student.
Motivation
The inability to handle the dynamic changes in the number and permutation of surroundings traffic participants may make it difficult for AVs to identify potential risks and adopt unsafe strategies. Moreover, the complex information at these intersections requires the AV to identify pivotal data to ascertain the timing of passage.
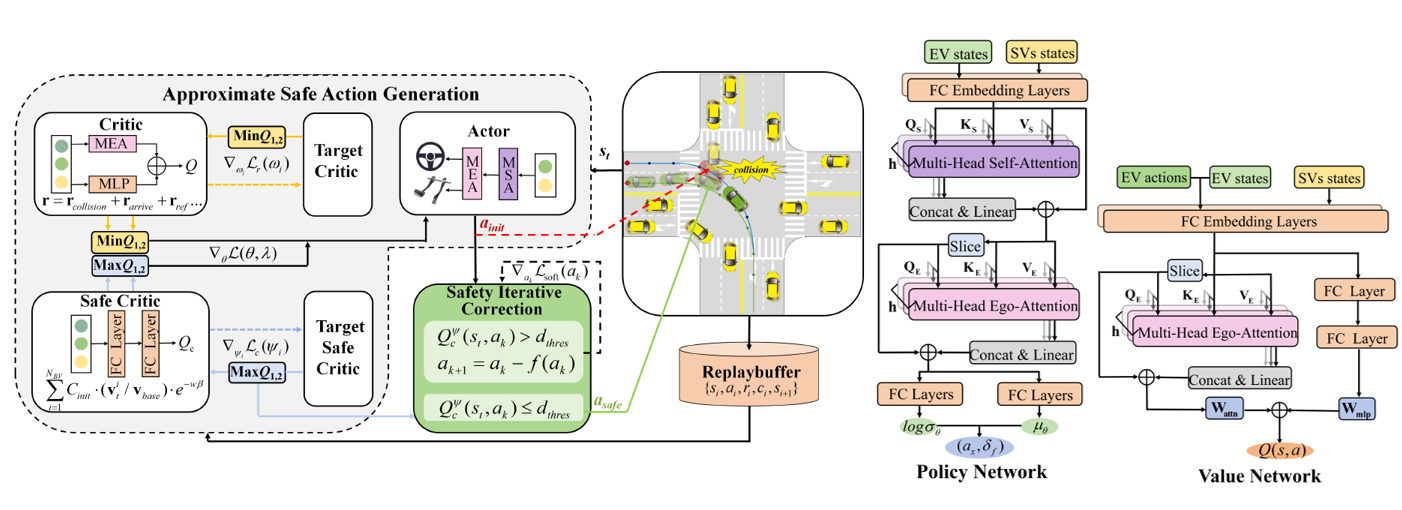
A risk-aware RL approach is proposed to improve safety and efficiency for driving through intersection.
Highlights
- Safe critics are constructed to evaluate driving risk and work in conjunction with the reward critic to update the actor.
- A Lagrangian relaxation method is incorporated to generate approximate safe actions, which are projected into a feasible safe region with safety iterative correction by cyclic gradient descent.
- A Multi-hop and Multi-layer perception mixed Attention Mechanism (MMAM) integrated into the actorcritic network enables the policy to adapt to dynamic traffic and overcome permutation sensitivity challenges, enhancing scene understanding and improving decision-making timing when navigating intersections.
Some Results
We compare Attention embedded and Risk-aware Soft Actor Critic (ARSAC) to the following baselines: SAC-RS, PPO-RS, which incorporate an auxiliary reward 𝐫_𝑠𝑎𝑓𝑒 compared to standard SAC and PPO; SAC-Lag and CPO. The implementation of SAC-Lag and CPO are based on Omnisafe Library.
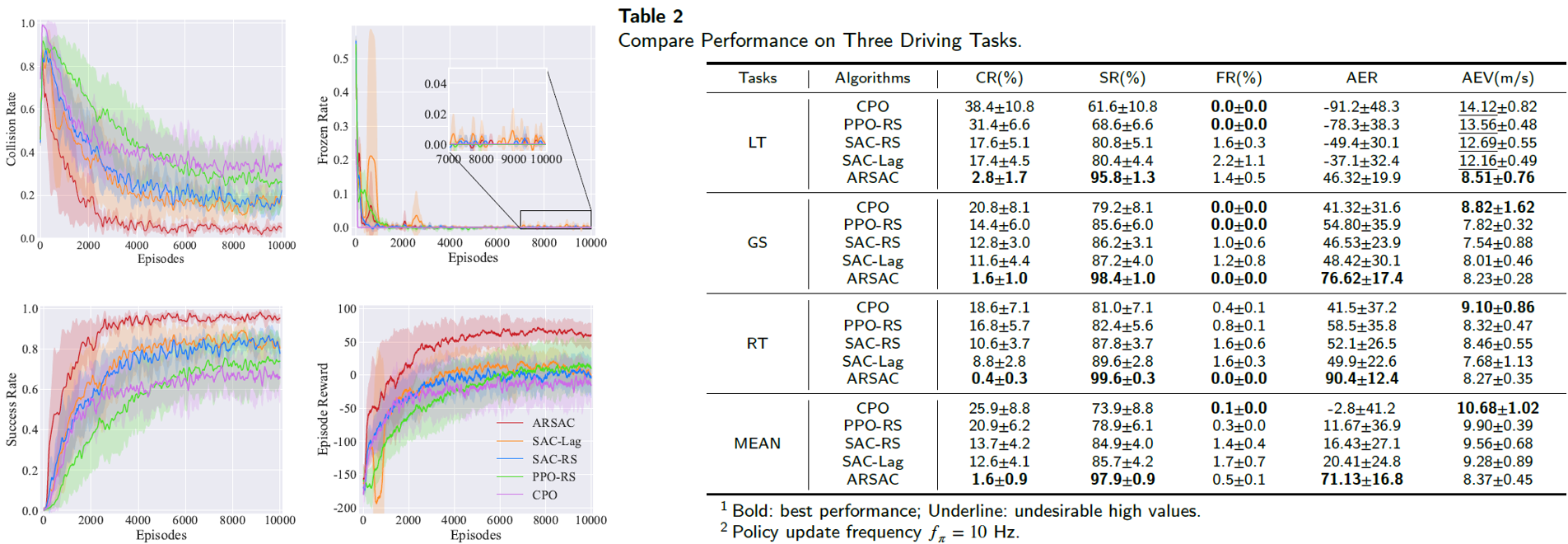
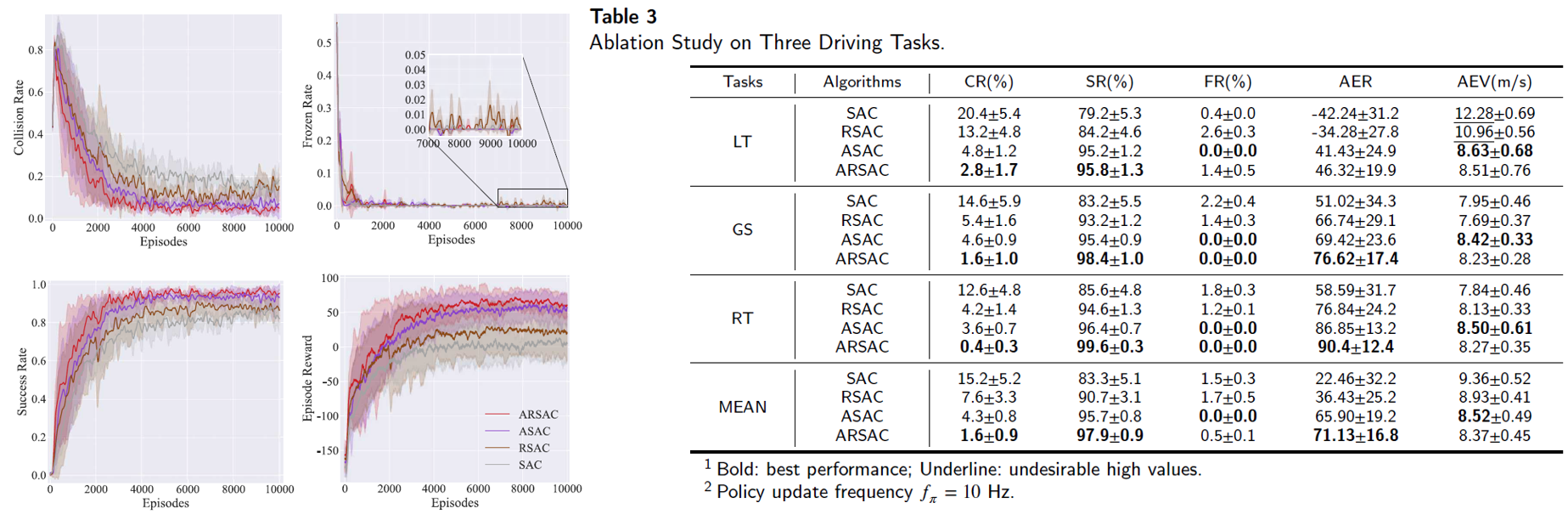
Results indicate that the proposed ARSAC algorithm outperforms or matches all other baseline algorithms across three driving tasks in terms of the final performance. Meanwhile, ablation studies demonstrate the specific role of different modules.
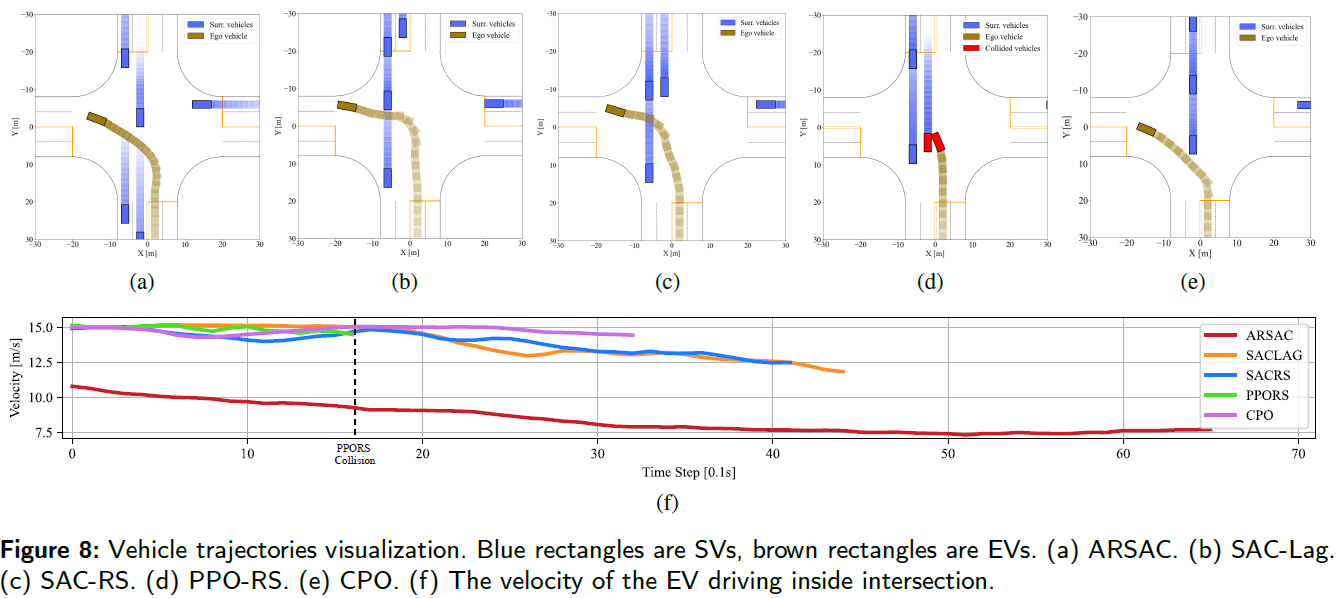
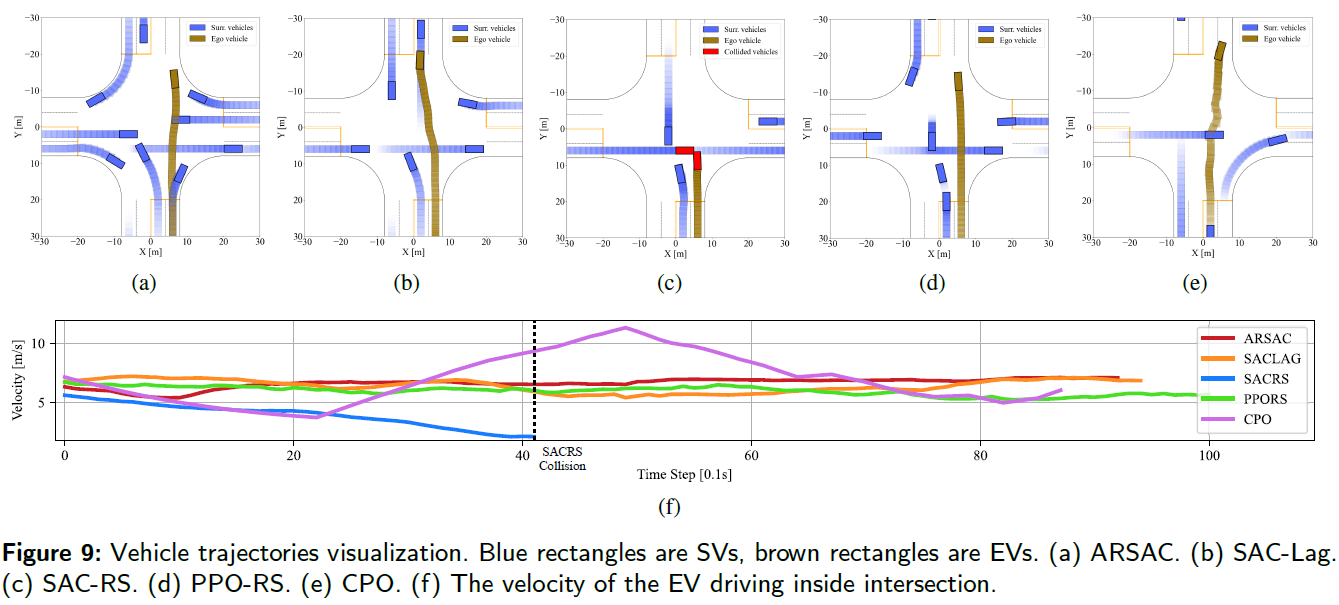
More details can be found in our recent paper “Risk-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving: Improving Safety When Driving through Intersection.” (under review) PDF
Current Work
- Combination CBF-based constraints and intrinsic reward optimization to accommodate safety and efficiency objectives.
- A learnable evaluation module to predict the anticipated risk.
Publications:
- Uncertainty-Aware Safety-Critical Decision and Control for Autonomous Vehicles at Unsignalized Intersections, Ran Yu, Zhuoren Li*, Lu Xiong, Wei Han and Bo Leng, IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Conf. (ITSC), 2025. (accept) arXiv
- Convergent Harmonious Decision: Lane Changing in a more Traffic Friendly Way, Ruolin Yang, Zhuoren Li, Bo Leng, Lu Xiong and Xin Xia, IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 20334-20347, 2025.
- Rule-Guidance Reinforcement Learning for Lane Change Decision-making: A Risk Assessment Approach, Lu Xiong, Zhuoren Li, Danyang Zhong, Puhang Xu and Chen Tang, Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2025, 38:30.
- Safe Reinforcement Learning of Lane Change Decision Making with Risk-Fused Constraint, Zhuoren Li, Lu Xiong, Bo Leng, Puhang Xu and Zhiqiang Fu, in Proc. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Conf. (ITSC), 2023, pp. 1313-1319.
Submitted/In Progress:
- Safety Enhanced Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving: Dare to Make Mistakes to Learn Faster and Better, Zhuoren Li, Jia Hu, Bo Leng, Lu Xiong and Puhang Xu, IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. (accepted)
- Uncertainty-Aware Safety-Critical Decision and Control for Autonomous Vehicles at Unsignalized Intersections, Ran Yu, Zhuoren Li*, Lu Xiong, Wei Han and Bo Leng, IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Conf. (ITSC), 2025. (accept)
- Safe Reinforcement Learning of Lane Change Decision Making with Risk-Fused Constraint, Zhuoren Li, Lu Xiong, Bo Leng, Puhang Xu and Zhiqiang Fu, in Proc. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Conf. (ITSC), 2023, pp. 1313-1319.